Sighing breathing is observed in subjects suffering from anxiety with no observed organic pathology. BC if Co2 is built up in blood it makes carbonic acid which decreases pH.

22 3 The Process Of Breathing Anatomy Physiology
Change in heart rate with breathing.

. This actually differs from faster breathing due to increased heart rate from exercise and it is this difference that makes breathe control a powerful way to lower your heart rate and stress simultaneously. By increasing the heart rate with a reflex. For example you can stop.
Forced breathing is an active mode of breathing which utilises additional muscles to rapidly expand and contract the thoracic cavity volume. Active inspiration involves the contraction of the accessory muscles of breathing in addition to those of quiet inspiration the diaphragm and external intercostals. This is reflected both during and following exercise.
The trigger for increased breathing rate is a drop in blood pH. Normal breathing is diaphragmatic allowing homogeneous inflation of both lungs with fresh air similar to what happens in the cylinder of a car engine due to the movement of the piston. Breathing very quickly especially faster than normal excessive drooling or difficulty swallowing skin that looks blue or gray around the nose mouth or fingernails noisy high-pitched breathing.
The size of chest cavity increase in inhalation and it decrease during exhalation. It most commonly occurs during exercise. Heart rate increases while breathing in and decreases while breathing out.
Overview and Key Difference 2. It causes a change in blood pressure and pulse rate in the main arteries. This rate can vary slightly with body position changes.
Consequently the breathing muscles are not active and the injured person can not breathe without the help of a ventilator. The breathing rate or the respiratory rate is determined as 12 to18 breaths per minute. However you can control your breathing voluntarily when you want to.
Periodic changes in lung volume were performed with frequencies from 30 to 120 respirations per minute rpm. From the graph we can see that the average heart rate of exercise at 20 minutes 30 seconds is around 171 bpm pace 353k and the average respiration rate is 36brpm. This maintains the normal respiratory rate of 12-15 breaths a minute.
The reason for this is because normally males are larger and taller than females due to their physical composition and unique male genetics. When people are stressed they tend to take faster more shallow breaths in accordance to increased heart rate. Effect of Body Position on Heart Rate A normal resting heart rate can be between 60 and 100 beats per minute says Peter Santucci MD professor of cardiology at Maywood Illinois-based Loyola University Medical Center.
This is to compensate for the decreased left ventricular output while breathing in. Normally you breathe automatically without even thinking about it. Suggest why this is an appropriate trigger to increase breathing rate.
Hence during diaphragmatic breathing all alveoli are homogeneously stretched vertically and get fresh air supply with higher O2 concentration for superior arterial blood oxygenation. Heart rate measures the contractions of a heart ie. A shallow breath called costal breathing requires contraction of the intercostal muscles.
This difference may be a consequence of the different orientation of the spinous processes which are more horizontal in females and more caudal in males. The volume of lungs increase during inhalation it means it gets inflated and it decreases during exhalation means it gets deflated. Breathing rate is regulated through the medullary respiratory center in response to demand for oxygen.
Many studies have tracked HRV in athletes some have used free spontaneous breathing whilst some use controlled paced breathing and they have all used a variety of different HRV measures making comparisons between studies very difficult or even impossible. How does forced breathing differ from quiet breathing. Your heart rate will still increase while exercising but not as sharply because the heart is strengthened.
Your breathing will intensify but you may be less winded. The key difference between inspiration and respiration is the inspiration is an active process which brings air into the lungs while the expiration is a passive process which excludes air out of the lungs. Eupnea is normal breathing.
Depending on your age and level of physical fitness a normal resting pulse ranges from 60 to 80 beats per minute. Since they are usually taller and larger they possess bigger lungs which means they have a greater surface area and more air sacs for gas exchange such as oxygen diffusion. In contrast forced breathing also known as hyperpnea is a mode of breathing that can occur during exercise or actions that require the active manipulation of breathing such as singing.
This is mainly because when at a faster pace the heart. Holding Your Breath Experiment 1. The difference between the fastest and the slowest heart rates was significantly larger in response to inspiration 217 - 73 beats per minute than in response to expiration 120 - 73 beats per minute.
During forced breathing the accessory muscles assist with inhalation. Exhalation involves contraction of the internal intercostal muscles. During the inhalation air rich in oxygen is taken into the blood but carbon dioxide is pushed out in exhalation process from the blood.
Hence the heart rate respiration rate 475 which is higher than the average value of 42 during this run. The rate and depth of breathing increases - this makes sure that more oxygen is absorbed into the blood and. A shallow breath called costal breathing requires contraction of the intercostal muscles.
Such greater dorsal orientation of the transverse processes of men may reorient the ribs leading to greater radial ribcage diameters 35. Forced breathing involves active inspiratory and expiratory movements. P less than 001.
On the other hand the pulse rate calculates the frequency in which palpable blood pressure surges in ones body. The heart rate increases during exercise. This sets the rhythm of breathing and contains neurons that are self-excitatory rather like the cells in the sino-atrial node in the heart and which fire off in a cycle.
Sighing is an involuntary inspiration that is 15 to 2 times greater than normal tidal volume. Furthermore a heartbeat pushes the blood throughout a human body. It has long been known that breathing affects heart rate variability HRV.
Brain to the breathing muscles. Most notably when you go from reclining to standing. Once your exercise routine is complete breathing and heart rate will return to normal more quickly.
In contrast forced breathing also known as hyperpnea is a mode of breathing that can occur during exercise or actions that require the active manipulation of breathing such as singing. Your breathing rate is measured in a. As the intercostal muscles relax air passively leaves the lungs.
During inspiration more blood gets pooled in the lungs so that left ventricle gets less blood to pump out. The abdominal muscles are involved during the maximum levels of forced breathing. The respiratory control centre is situated in the medulla oblongata of the brain.
As the intercostal muscles relax air passively leaves the lungs.
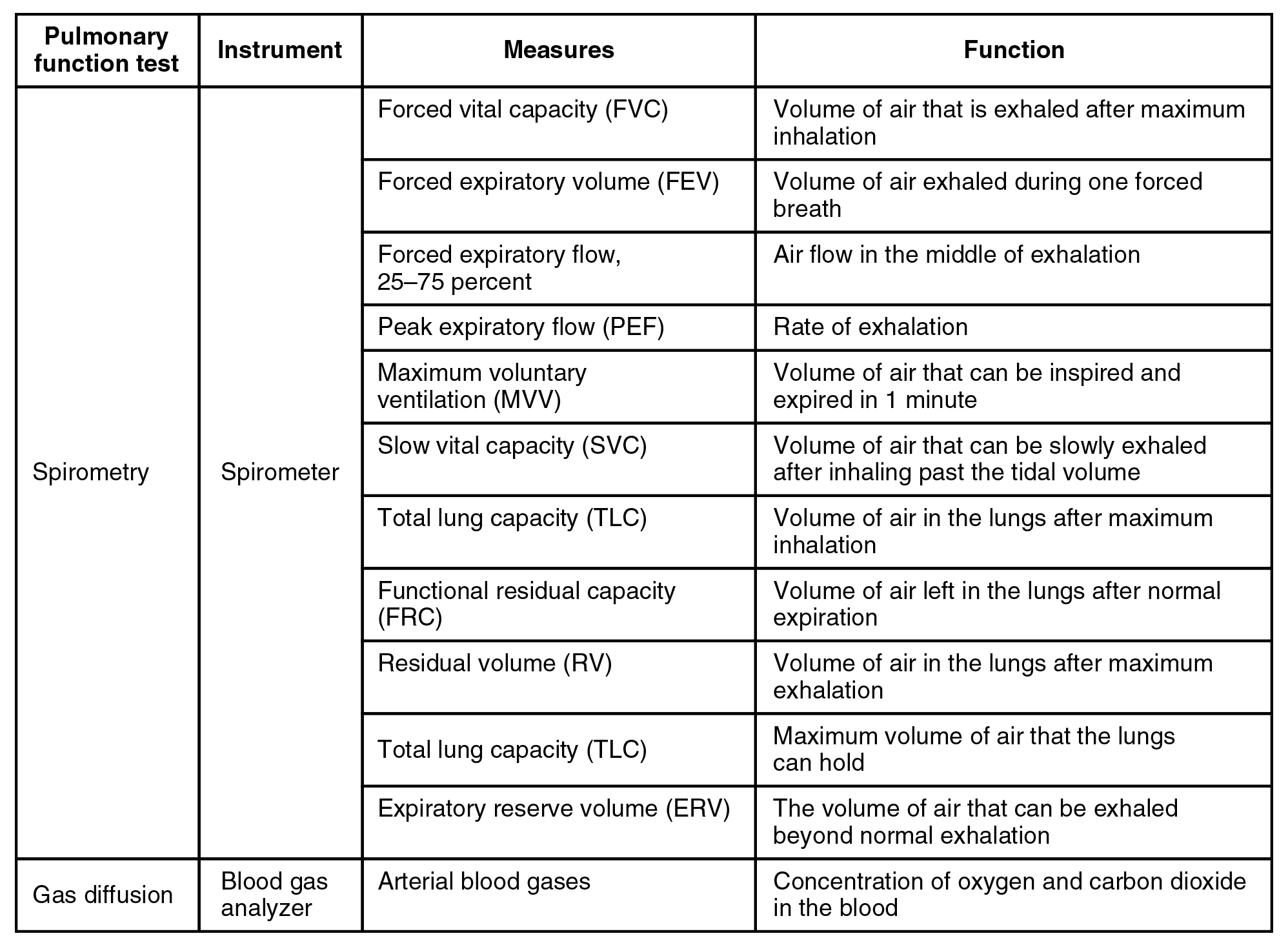
The Process Of Breathing Anatomy And Physiology
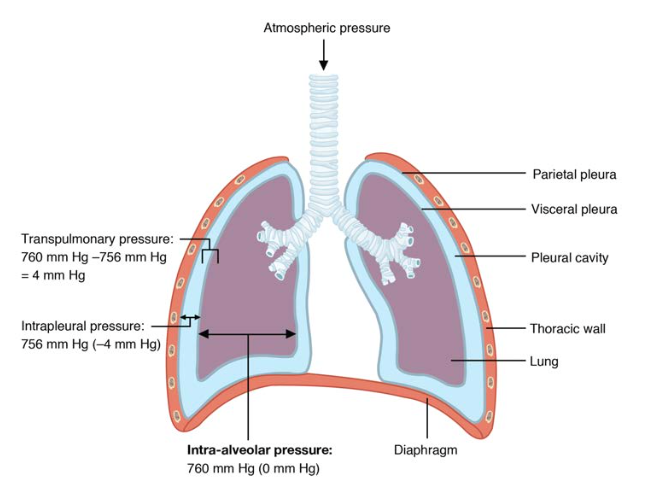
0 Comments